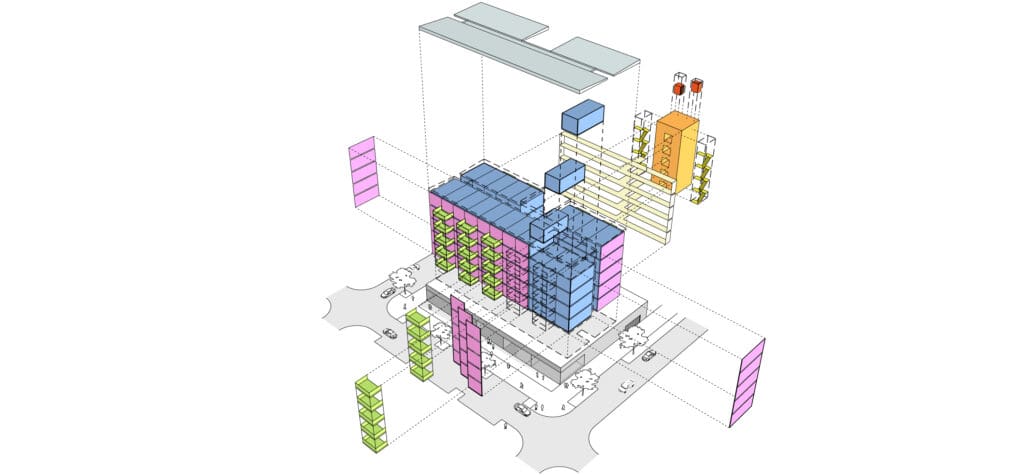
1. Robotics in Modular Construction
The integration of robotics in modular construction marks a significant leap towards efficiency and precision. Robots, as those utilised at Modbotics1, are increasingly used to speed up the production of building components like walls, floors and ceiling.
This kind of automation can bring costs down by 30%, quicken delivery times by 50%, and reduce waste by up to 70%2. As robotics technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in modular construction capabilities, reducing human error and increasing safety on production lines.